In the landscape of modern manufacturing and innovation, 3D printing technology stands out as a revolutionary force, reshaping industries, fueling creativity, and unlocking new possibilities. Also known as additive manufacturing, 3D printing enables the fabrication of three-dimensional objects layer by layer from digital designs, offering unprecedented flexibility, speed, and customization. In this article, we delve into the transformative potential of 3D printing technology, exploring its applications, benefits, and future prospects.
Origins and Evolution of 3D Printing:
The roots of 3D printing technology can be traced back to the 1980s when the first additive manufacturing processes were developed for rapid prototyping in the aerospace and automotive industries. Since then, 3D printing has undergone significant advancements, driven by innovations in materials science, software development, and hardware design.
Today, 3D printing encompasses a diverse range of technologies and processes, including fused deposition modeling (FDM), stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and digital light processing (DLP). Each of these techniques offers unique advantages and capabilities, catering to different applications and requirements.
Applications Across Industries:
The versatility of 3D printing has led to its adoption across a wide range of industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to aerospace and consumer goods. Some notable applications of 3D printing technology include:
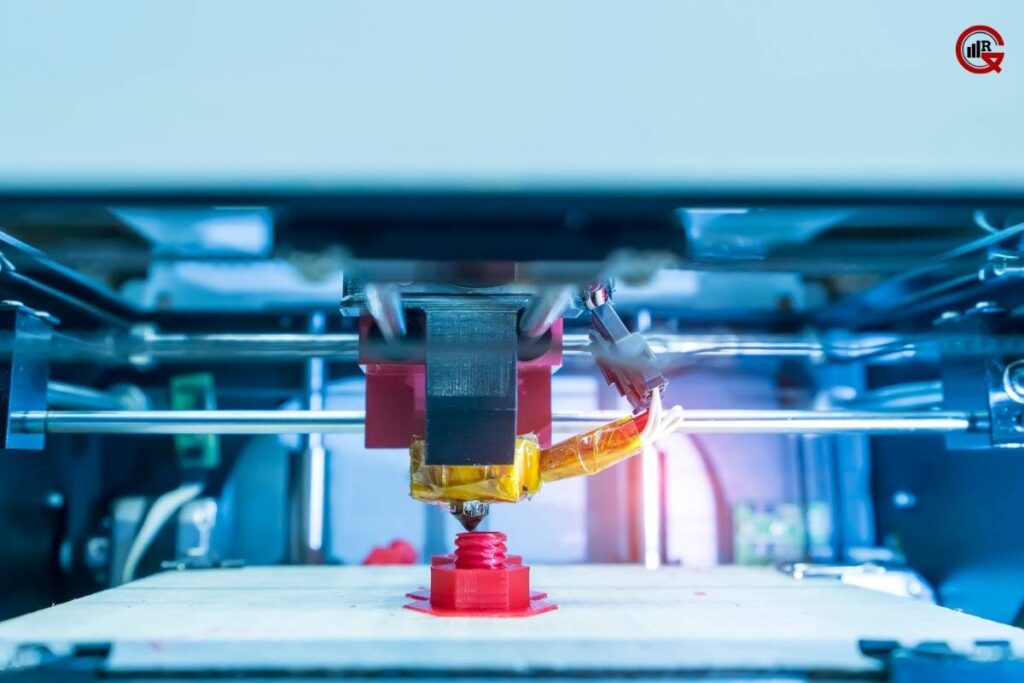

- Prototyping and Product Development: 3D printing enables rapid prototyping and iterative design, allowing companies to accelerate the development cycle and bring products to market faster. By producing functional prototypes with high precision and accuracy, manufacturers can test concepts, validate designs, and identify potential issues early in the process.
- Custom Manufacturing and Personalization: One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing is its ability to customize products according to individual preferences and specifications. Whether it’s tailored prosthetics, bespoke jewelry, or personalized consumer electronics, 3D printing allows for on-demand manufacturing and mass customization, catering to diverse needs and tastes.
- Healthcare and Biomedical Applications: In the healthcare sector, 3D printing technology is revolutionizing patient care by enabling the production of custom implants, surgical guides, and anatomical models. Surgeons can use 3D-printed models to plan complex procedures, visualize patient-specific anatomy, and improve surgical outcomes. Moreover, researchers are exploring the potential of 3D bioprinting to fabricate living tissues and organs for transplantation, paving the way for regenerative medicine.
- Aerospace and Automotive Engineering: The aerospace and automotive industries have embraced 3D printing technology for prototyping, tooling, and manufacturing of lightweight components. Additive manufacturing allows engineers to design complex geometries, optimize part performance, and reduce material waste, leading to cost savings and improved fuel efficiency.
Advantages of 3D Printing Technology:
The widespread adoption of 3D printing technology can be attributed to its numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. Some key benefits of 3D printing include:
- Design Freedom: Unlike subtractive manufacturing techniques, which are limited by tooling and machining constraints, 3D printing offers unparalleled design freedom. Complex geometries, internal structures, and organic shapes can be easily fabricated using additive manufacturing processes, allowing designers to explore new possibilities and push the boundaries of innovation.
- Rapid Prototyping: Traditional prototyping methods often require costly tooling and lengthy lead times, making it difficult to iterate and refine designs quickly. In contrast, 3D printing enables rapid prototyping with minimal setup time and low material waste, enabling designers to test concepts, validate assumptions, and make adjustments on the fly.
- Customization and Personalization: With 3D printing, each object can be customized to meet the specific needs and preferences of the end-user. Whether it’s adjusting the size, shape, or material properties, 3D printing allows for on-demand manufacturing of personalized products, enhancing user experience and satisfaction.
- Reduced Waste and Environmental Impact: Additive manufacturing processes generate less waste compared to traditional manufacturing methods, as they only use the material required to build the desired object. Moreover, 3D printing enables the use of recycled and biodegradable materials, further reducing the environmental footprint of manufacturing operations.
Challenges and Limitations:
Despite its many advantages, 3D printing technology also faces several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed for widespread adoption and scalability. Some of these challenges include:
- Material Limitations: While the range of 3D printable materials has expanded in recent years, there are still limitations in terms of material properties, compatibility, and performance. Certain materials may be unsuitable for specific applications due to factors such as strength, durability, or heat resistance.
- Post-Processing Requirements: 3D printed parts often require post-processing steps such as sanding, polishing, or painting to achieve the desired surface finish and appearance. These additional steps can add time and cost to the manufacturing process, particularly for high-volume production runs.
- Quality Control and Certification: Ensuring the quality and reliability of 3D printed parts is essential, especially in safety-critical industries such as aerospace and healthcare. However, establishing quality control protocols and obtaining certification for additive manufacturing processes can be challenging due to the lack of standardized testing methods and regulatory frameworks.
- Cost and Scalability: While 3D printing offers significant advantages in terms of design flexibility and customization, it can still be more expensive than traditional manufacturing methods for certain applications, particularly for large-scale production runs. Additionally, scaling up additive manufacturing operations to meet growing demand may require significant investment in equipment, infrastructure, and training.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends:
Looking ahead, the future of 3D printing technology is bright, with numerous emerging trends and developments poised to drive further innovation and adoption. Some key areas to watch include:
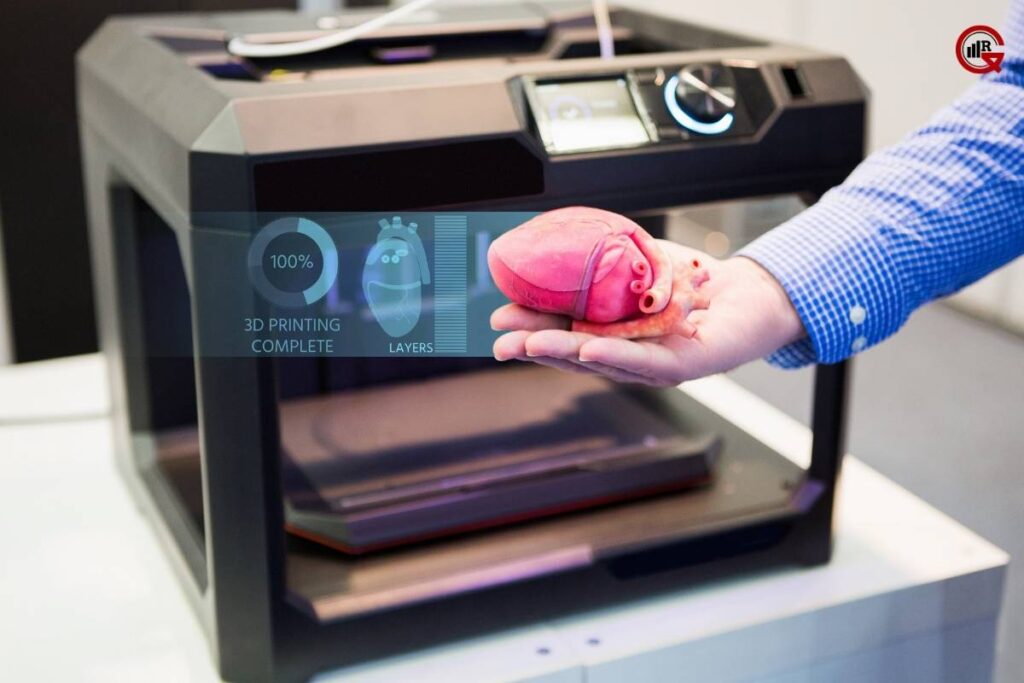

- Advanced Materials and Composites: Researchers are exploring new materials and composites with enhanced properties for 3D printing applications, such as high-strength polymers, metal alloys, and bio-compatible ceramics. These materials could expand the range of applications for additive manufacturing and unlock new opportunities in areas such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
- Multi-Material Printing: Multi-material 3D printing enables the fabrication of complex structures with diverse material properties, such as soft and rigid components or conductive and insulating layers. By integrating different materials within a single print, designers can create functional prototypes, electronic devices, and biomedical implants with unprecedented versatility and functionality.
- Digital Twin Technology: Digital twin technology enables the creation of virtual replicas of physical objects or systems, allowing designers to simulate, analyze, and optimize performance in real time. By combining 3D printing with digital twin technology, manufacturers can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and reliability in the design and production of complex products and systems.
- Distributed Manufacturing Networks: The rise of distributed manufacturing networks and on-demand production models is transforming the way goods are designed, produced, and distributed. By decentralizing manufacturing operations and leveraging local resources, companies can reduce lead times, minimize transportation costs, and respond more quickly to market demand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing technology represents a paradigm shift in manufacturing and innovation, offering unprecedented capabilities for design freedom, customization, and sustainability. From aerospace engineering to healthcare, the applications of 3D printing are vast and diverse, with the potential to revolutionize industries and transform the way we design, produce, and consume goods. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements in materials science, software development, and process optimization are paving the way for a future where additive manufacturing plays an increasingly central role in our lives. As we continue to explore the possibilities of 3D printing technology, it’s clear that the only limit to its potential is our imagination.






