Source – AnkerMake
In the realm of modern manufacturing and creativity, 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology, enabling the fabrication of intricate objects with unprecedented precision and efficiency. At the heart of this revolution lies 3D printing design software, the digital toolkit that empowers designers, engineers, and enthusiasts to bring their visions to life in three-dimensional form. In this article, we explore the landscape of 3D printing design software, uncovering its capabilities, features, and the creative possibilities it unlocks.
Introduction to 3D Printing Software
Before diving into the intricacies of 3D printing software, it’s essential to understand its fundamental role in the 3D printing process. At its core, 3D printing design software serves as the bridge between the digital realm and the physical world, allowing users to create, modify, and optimize digital models that can be translated into physical objects through additive manufacturing.
From simple geometric shapes to complex assemblies, 3D printing design software accommodates a wide range of design requirements and skill levels, making it accessible to novices and experts alike. Whether you’re a hobbyist experimenting with DIY projects or a professional engineer developing prototypes for a new product, there’s a 3D printing design suite tailored to your needs.
Key Features and Functionality
The best 3D printing design software offers a comprehensive suite of features and functionality designed to streamline the design process and maximize creativity. Some of the key features to look for in 3D printing design include:
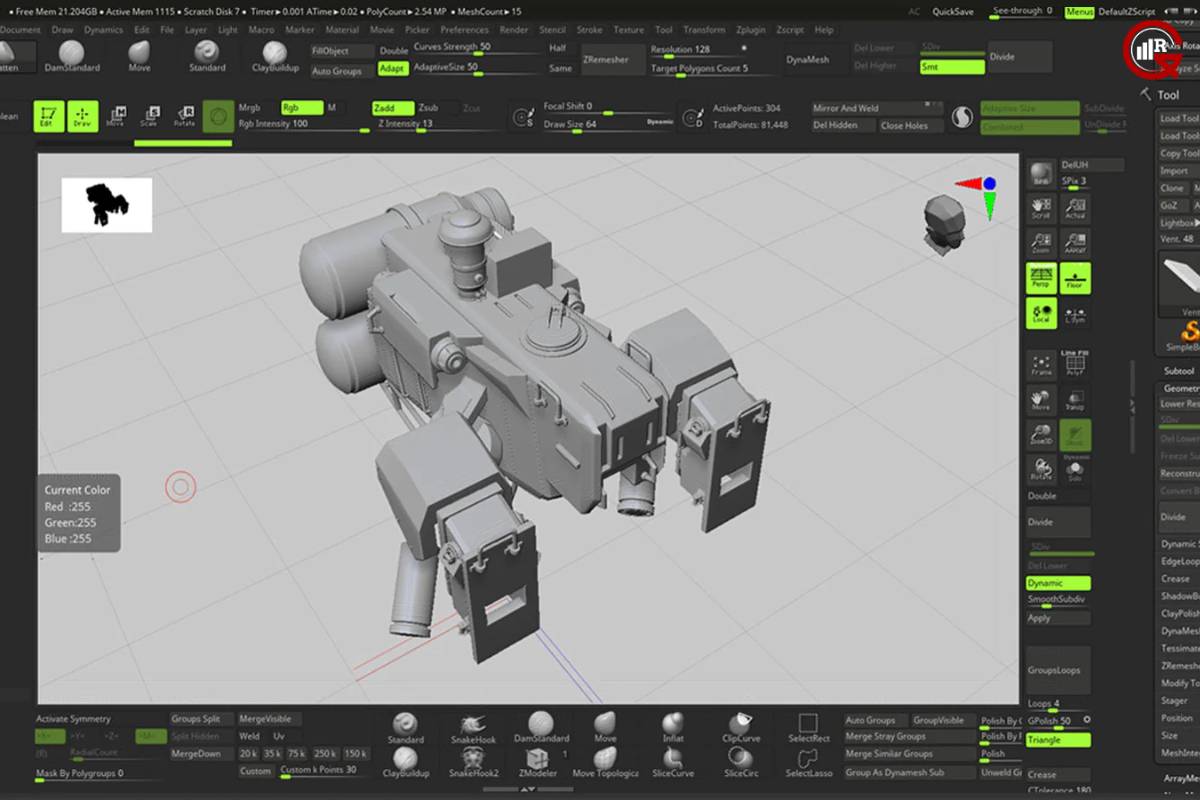
- Intuitive User Interface: A user-friendly interface with intuitive navigation tools and easy-to-understand commands is essential for beginners and experienced users alike.
- Modeling Tools: Robust modeling tools for creating and manipulating 3D geometry, including tools for extrusion, lofting, sweeping, and sculpting.
- Parametric Design: Parametric modeling capabilities that allow users to define geometric relationships and constraints, enabling rapid iteration and design optimization.
- Support for Multiple File Formats: Compatibility with a wide range of file formats, including STL, OBJ, STEP, and IGES, to facilitate seamless collaboration and interoperability with other software applications.
- Advanced Rendering and Visualization: High-quality rendering and visualization tools that allow users to create realistic renderings of their designs, helping to communicate ideas and concepts effectively.
- Mesh Repair and Analysis: Built-in tools for repairing and analyzing mesh geometry to ensure watertight models suitable for 3D printing without errors or defects.
- Integration with 3D Printing Hardware: Integration with 3D printing hardware and slicer software, allowing users to prepare models for printing directly within the design environment.
Popular 3D Printing Software
There is a plethora of 3D printing softwares available in the market, catering to different needs, preferences, and budgets. Some of the most popular 3D printing design software packages include:
- Autodesk Fusion 360: A cloud-based CAD/CAM platform that offers a comprehensive set of design tools for mechanical engineering, industrial design, and product development.
- Blender: A powerful open-source 3D modeling and animation software suite that is widely used by artists, designers, and animators for creating complex 3D models and visualizations.
- SolidWorks: A professional-grade CAD software package known for its robust parametric modeling capabilities and extensive library of design features and tools.
- Tinkercad: A beginner-friendly web-based 3D modeling software platform that is ideal for educators, students, and hobbyists looking to learn the basics of 3D design and printing.
- Rhino: A versatile 3D modeling software package popular among architects, industrial designers, and jewelry designers for its flexible modeling tools and support for organic shapes.
- SketchUp: An intuitive 3D modeling software package that is widely used by architects, interior designers, and hobbyists for creating detailed 3D models of buildings, furniture, and other objects.
Creative Applications and Use Cases
The versatility of 3D printing software extends far beyond traditional manufacturing and engineering applications. From art and fashion to healthcare and education, 3D printing design software is empowering individuals and organizations to innovate and create in unprecedented ways.
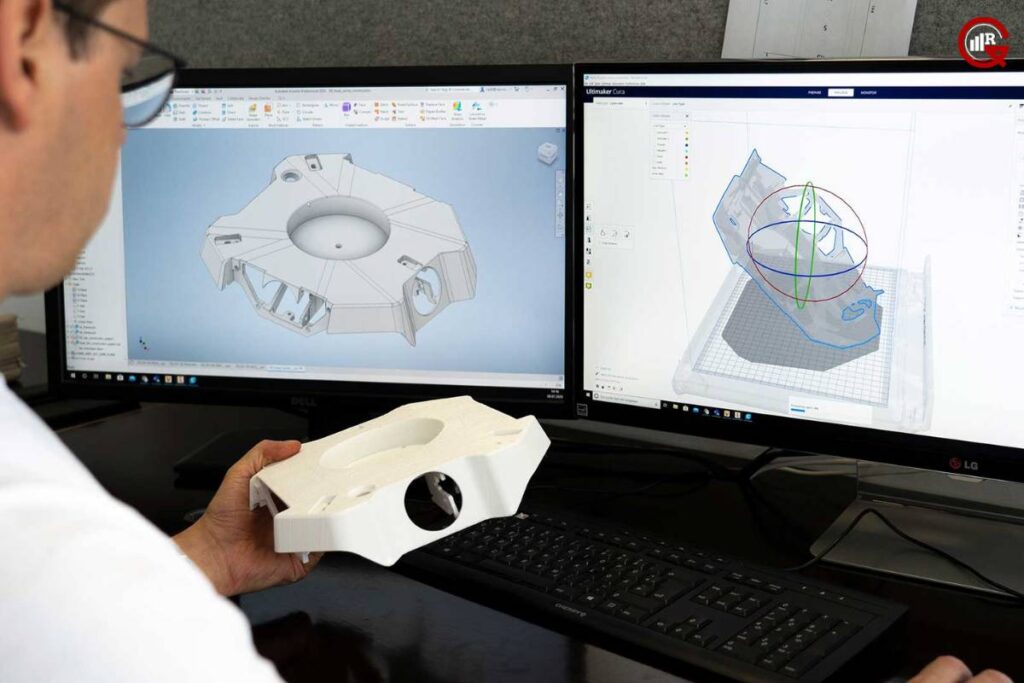

- Art and Sculpture: Artists and sculptors are using 3D printing software to create intricate sculptures, installations, and mixed-media artworks that push the boundaries of creativity and expression.
- Fashion and Wearable Technology: Designers are leveraging 3D printing software to create bespoke fashion accessories, jewelry, and wearable technology that blend cutting-edge design with functional innovation.
- Healthcare and Biomedical Engineering: Researchers and medical professionals are harnessing the power of 3D printing design software to develop customized prosthetics, implants, and surgical guides that improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
- Education and STEM Learning: Educators are integrating 3D printing software into STEM curricula to engage students in hands-on learning experiences and foster creativity, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills.
Future Trends and Developments
As technology continues to evolve and new advancements emerge, the landscape of 3D printing design is poised for further innovation and growth. Some of the key trends and developments shaping the future of 3D printing design include:
Artificial Intelligence and Generative Design: The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms into 3D printing design software is enabling generative design capabilities that automatically generate optimized design solutions based on user-defined criteria and constraints.
Cloud-Based Collaboration and Workflow Automation: Cloud-based collaboration tools and workflow automation solutions are streamlining the design process and facilitating real-time collaboration between remote teams, enabling faster iteration and design iteration.
Integration with Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality: Integration with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies is enabling designers to visualize and interact with 3D models in immersive virtual environments, enhancing the design review process and enabling more intuitive design exploration.
Moreover, 3D printing design software enables on-demand manufacturing, eliminating the need for costly inventory management and reducing the risk of overproduction and waste. By leveraging digital manufacturing technologies, companies can respond quickly to changing market demands and offer consumers a wider range of options for personalized products.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 3D printing design software is a powerful tool that is driving innovation and creativity across a wide range of industries and disciplines. From mechanical engineering to art and fashion, the capabilities of 3D printing software are virtually limitless, empowering individuals and organizations to bring their ideas to life in ways that were once unimaginable.
As technology continues to advance and new developments emerge, the future of 3D printing design promises to be even more exciting and transformative. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a novice enthusiast, there has never been a better time to explore the world of 3D printing design and unleash your creativity on the digital frontier.






