In an era where technology permeates every aspect of our lives, agriculture is no exception. The emergence of smart farming, powered by the Internet of Things (IoT), has revolutionized traditional agricultural practices, offering innovative solutions to age-old challenges. This article explores the fundamentals of smart farming and delves into how IoT is transforming agriculture, from field monitoring to crop management and beyond.
Understanding Smart Farming and IoT
Smart farming, also known as precision agriculture, is an approach that utilizes technology to optimize farming operations and improve efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. At the core of smart farming is the integration of IoT devices, which enable the collection, analysis, and utilization of real-time data from various sources, such as sensors, drones, and satellite imagery.
IoT devices in agriculture are interconnected through wireless networks, allowing farmers to remotely monitor and control farm operations from anywhere with an internet connection. This seamless connectivity and data exchange enables farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and respond promptly to changing environmental conditions.
Applications of IoT in Smart Farming
IoT technology finds a wide range of applications across the agricultural smart farming value chain, revolutionizing traditional farming practices and enhancing productivity and sustainability. Some key applications of IoT in agriculture include:
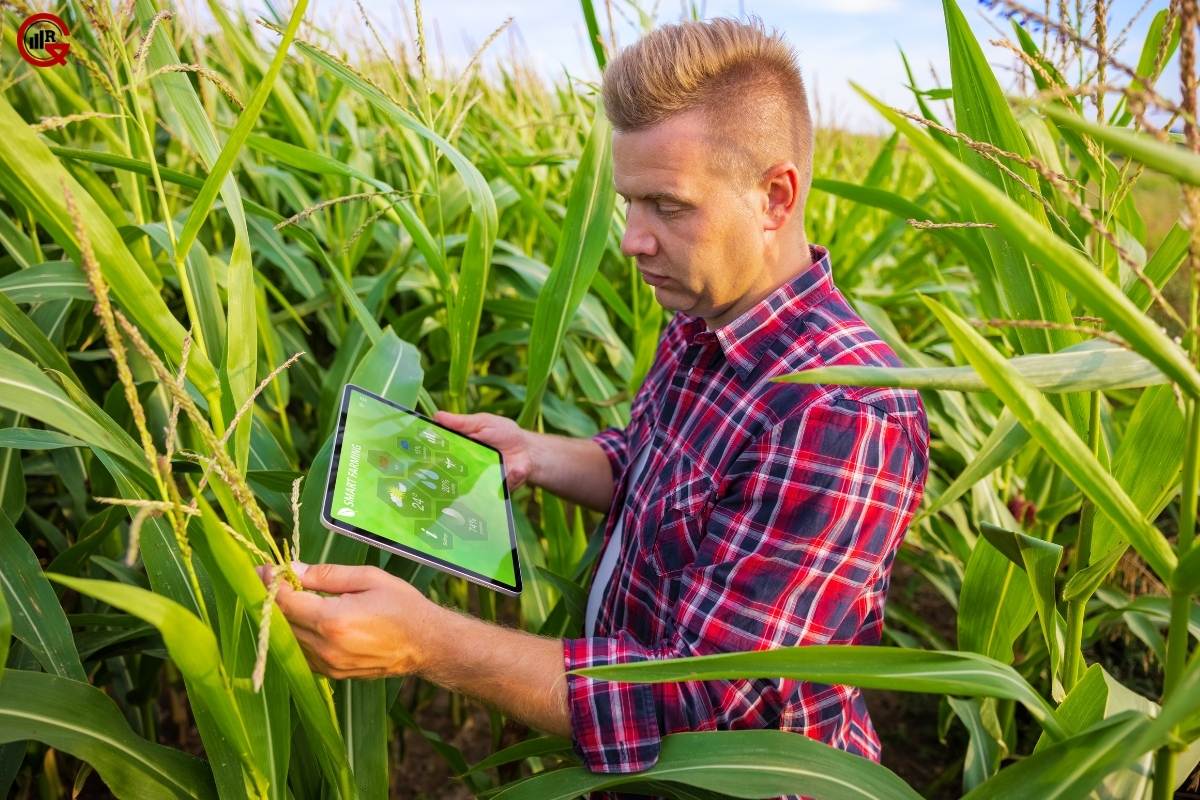

1. Precision Farming:
IoT sensors monitor soil moisture, temperature, nutrient levels, and other environmental parameters in real time, enabling farmers to implement precision irrigation and fertilization strategies. By delivering water and nutrients precisely where and when they are needed, precision farming minimizes waste and maximizes crop yields.
2. Crop Monitoring and Management:
IoT devices such as drones and satellite imagery provide farmers with detailed insights into crop health, growth patterns, and pest infestations. This information allows farmers to detect early signs of stress or disease, implement targeted pest control measures, and optimize harvesting schedules for maximum yield and quality.
3. Livestock Monitoring:
IoT sensors of smart farming attached to livestock animals monitor vital signs, behavior, and location in real-time, enabling farmers to detect signs of illness, monitor grazing patterns, and ensure animal welfare. By leveraging IoT technology, farmers can optimize feeding schedules, detect early signs of disease, and prevent livestock losses.
4. Supply Chain Management:
IoT devices track and monitor agricultural products throughout the supply chain, from farm to fork. By providing real-time visibility into product location, temperature, and condition, IoT technology enables farmers, distributors, and retailers to ensure product quality, reduce waste, and enhance traceability and transparency.
5. Environmental Monitoring:
IoT sensors monitor environmental conditions such as weather patterns, air quality, and soil erosion, providing valuable insights into the impact of farming practices on ecosystems and natural resources. By monitoring and mitigating environmental risks, farmers can minimize their ecological footprint and contribute to sustainable agriculture and conservation efforts.
Benefits of IoT in Smart Farming
The adoption of IoT technology in agriculture offers numerous benefits for farmers, consumers, and the environment. Some key benefits include:
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
IoT-enabled precision farming practices optimize resource utilization, reduce input costs, and maximize crop yields, enhancing overall farm efficiency and profitability.
2. Improved Decision-Making:
Real-time data from IoT sensors enable farmers to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information, leading to better crop management, risk mitigation, and resource allocation.
3. Enhanced Sustainability:
IoT technology enables farmers to adopt sustainable farming practices that minimize environmental impact, conserve natural resources, and promote biodiversity, contributing to long-term environmental sustainability.
4. Enhanced Food Safety and Quality:
IoT devices ensure product traceability and transparency throughout the supply chain, enabling farmers, distributors, and consumers to track the origin, handling, and condition of agricultural products, thereby ensuring food safety and quality.
5. Resilience to Climate Change:
IoT sensors provide early warning systems for extreme weather events, droughts, and other climate-related risks, enabling farmers to adapt and respond proactively to changing environmental conditions, enhancing resilience, and reducing vulnerability to climate change impacts.
Challenges and Deliberations
Despite the many benefits of IoT in agriculture, several challenges and considerations must be addressed for widespread adoption and effectiveness. These include:
1. Cost and Affordability:
The initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs of IoT devices can be prohibitive for smallholder farmers or those operating on a limited budget. Efforts to reduce costs, increase affordability, and provide financial incentives or subsidies for IoT in smart farming adoption are needed to ensure equitable access to technology.
2. Data Privacy and Security:
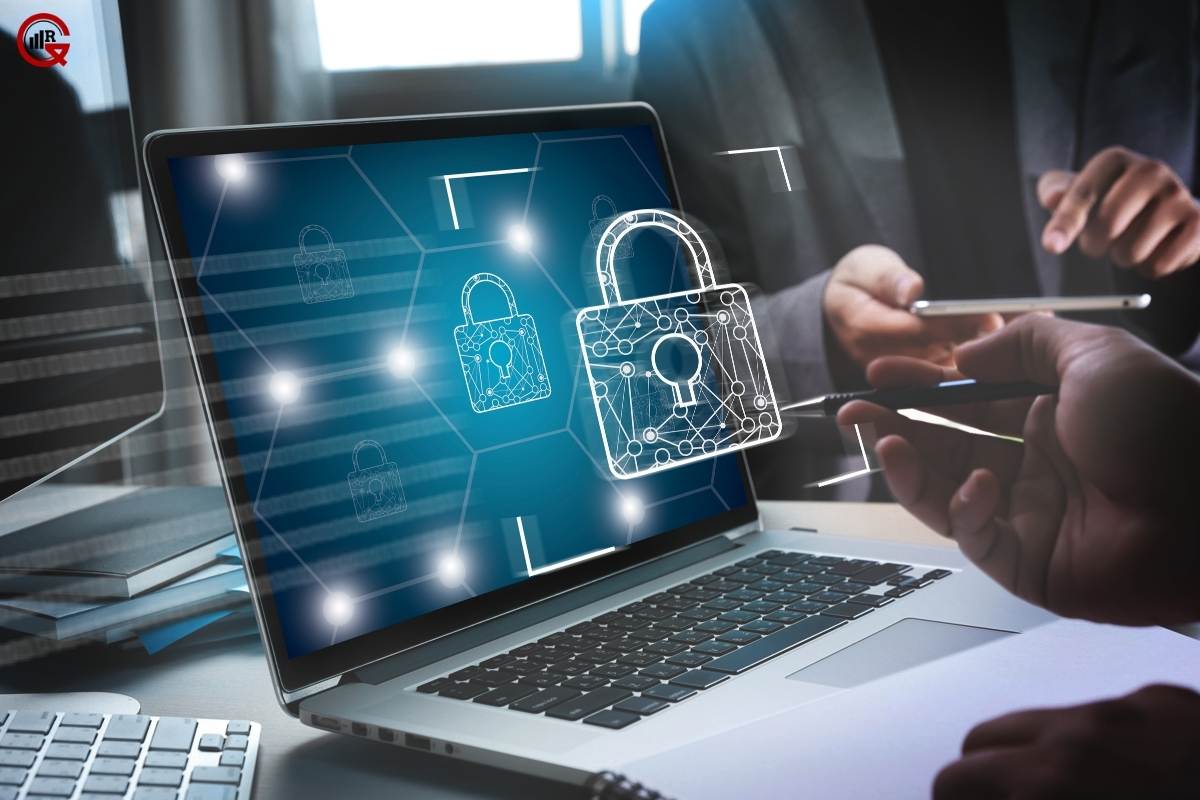

IoT devices collect and transmit sensitive data about farm operations, crop yields, and supply chain activities, raising concerns about data privacy and security. Robust data encryption, secure communication protocols, and adherence to data protection regulations are essential to safeguarding farmers’ data and maintaining trust in IoT technology.
3. Interoperability and Compatibility:
IoT devices in smart farming from different manufacturers may use proprietary protocols or standards, leading to interoperability issues and compatibility challenges. Establishing common standards, open APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), and interoperable platforms is essential for seamless integration and data exchange between IoT devices and systems.
4. Digital Literacy and Technical Skills:
Many farmers lack the digital literacy and technical skills needed to effectively deploy and utilize IoT technology. Training programs, extension services, and capacity-building initiatives are needed to enhance farmers’ digital literacy and technical skills, enabling them to harness the full potential of IoT in agriculture.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of IoT in agriculture looks promising, with continued advancements in technology, research, and innovation driving the development and adoption of IoT solutions tailored to the needs of farmers and agribusinesses. From advanced sensors and drones to AI-powered analytics and blockchain-based traceability systems, IoT is poised to transform agriculture, making it more efficient, sustainable, and resilient in the face of emerging challenges and opportunities.
In conclusion, IoT technology in smart farming is revolutionizing agriculture, empowering farmers to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource utilization, and enhance productivity, sustainability, and resilience. By harnessing the power of IoT, agriculture has the potential to feed the world’s growing population while protecting the planet for future generations.
However, realizing this potential requires addressing challenges such as cost, privacy, interoperability, and digital literacy, and fostering collaboration and innovation across the agricultural ecosystem. With concerted efforts and investments, IoT holds the key to unlocking a smarter, more sustainable, and more resilient future for agriculture and food security worldwide.






