In an era defined by technological innovation, the fusion of 3D printing with Jewelry design has created a transformative impact on the world of fashion and luxury. 3D printed Jewelry is revolutionizing the way designers conceptualize, create, and bring their visions to life. This article explores the intricate world of 3D printed Jewelry, examining its fabrication process, advantages, applications, and the future potential of this cutting-edge technology.
Understanding 3D Printing in Jewelry:
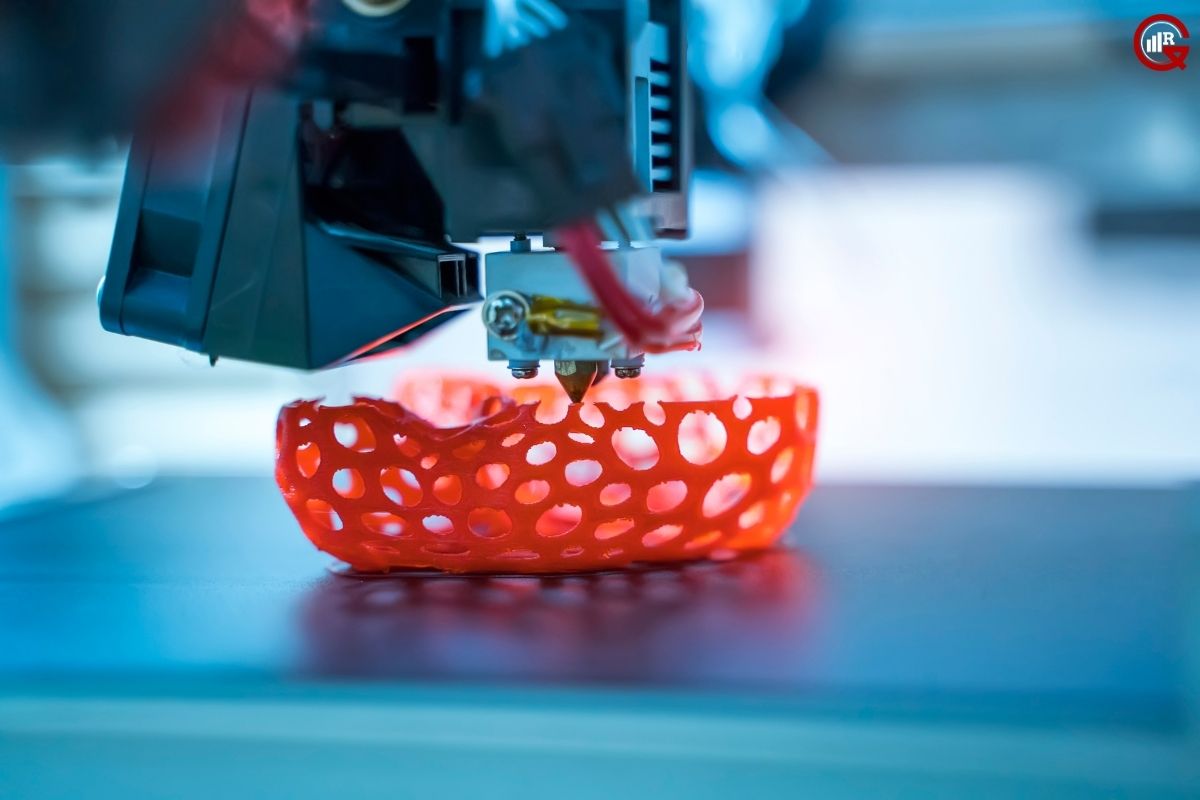
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves building three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. In Jewelry design, this process allows for the creation of intricate, customized pieces that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods. The fabrication process typically includes the following steps:
Design and Modeling: Jewelry designers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to create detailed digital models of their designs. This digital approach allows for precise control over every aspect of the piece, from complex geometries to delicate patterns.
Material Selection: Depending on the desired final product, designers choose from a variety of materials, including precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum, as well as innovative materials such as resin and biocompatible polymers.
Printing Process: Several 3D printing technologies are employed in Jewelry making, including stereolithography (SLA), selective laser sintering (SLS), and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS). Each technology offers unique advantages in terms of detail resolution, material compatibility, and production speed.
Post-Processing: After printing, the raw piece undergoes post-processing steps such as polishing, plating, and setting of gemstones. These finishing touches ensure the final product meets the high standards of quality and aesthetics expected in the Jewelry industry.
Quality Control and Customization: The final step involves rigorous quality control to ensure each piece meets design specifications and customer expectations. The ability to easily customize designs means that pieces can be tailored to individual preferences, making each item unique.

Advantages of 3D Printed Jewelry:
3D printed Jewelry offers several significant advantages over traditional manufacturing methods:
Design Freedom: One of the most compelling benefits is the ability to create complex, intricate designs that are challenging to produce using conventional techniques. This opens up new possibilities for creativity and innovation in Jewelry design.
Customization: 3D printing allows for unprecedented levels of customization. Customers can personalize their Jewelry with specific designs, engravings, and modifications, ensuring a truly unique piece.
Rapid Prototyping: Designers can quickly produce prototypes to test new designs and make adjustments before final production. This accelerates the design process and allows for more experimentation and innovation.
Material Efficiency: Additive manufacturing is inherently material-efficient, as it builds objects layer by layer, minimizing waste. This is particularly important in Jewelry making, where the cost of precious metals can be high.
Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment in 3D printing technology can be significant, the ability to produce detailed designs without the need for expensive molds and tooling can lead to cost savings over time.
Current Applications:
The versatility of 3D printing technology has led to its adoption in various aspects of Jewelry design and manufacturing:
Custom Jewelry: 3D printing is ideal for creating bespoke Jewelry pieces tailored to individual preferences. From engagement rings to personalized pendants, customers can collaborate with designers to bring their unique visions to life.
Intricate Designs: Designers are using 3D printing to create intricate, avant-garde pieces that push the boundaries of traditional Jewelry design. This includes complex lattice structures, organic forms, and detailed filigree work.
Prototyping and Experimentation: 3D printing allows designers to rapidly prototype new concepts and experiment with different forms and materials. This iterative process leads to more innovative and refined final products.
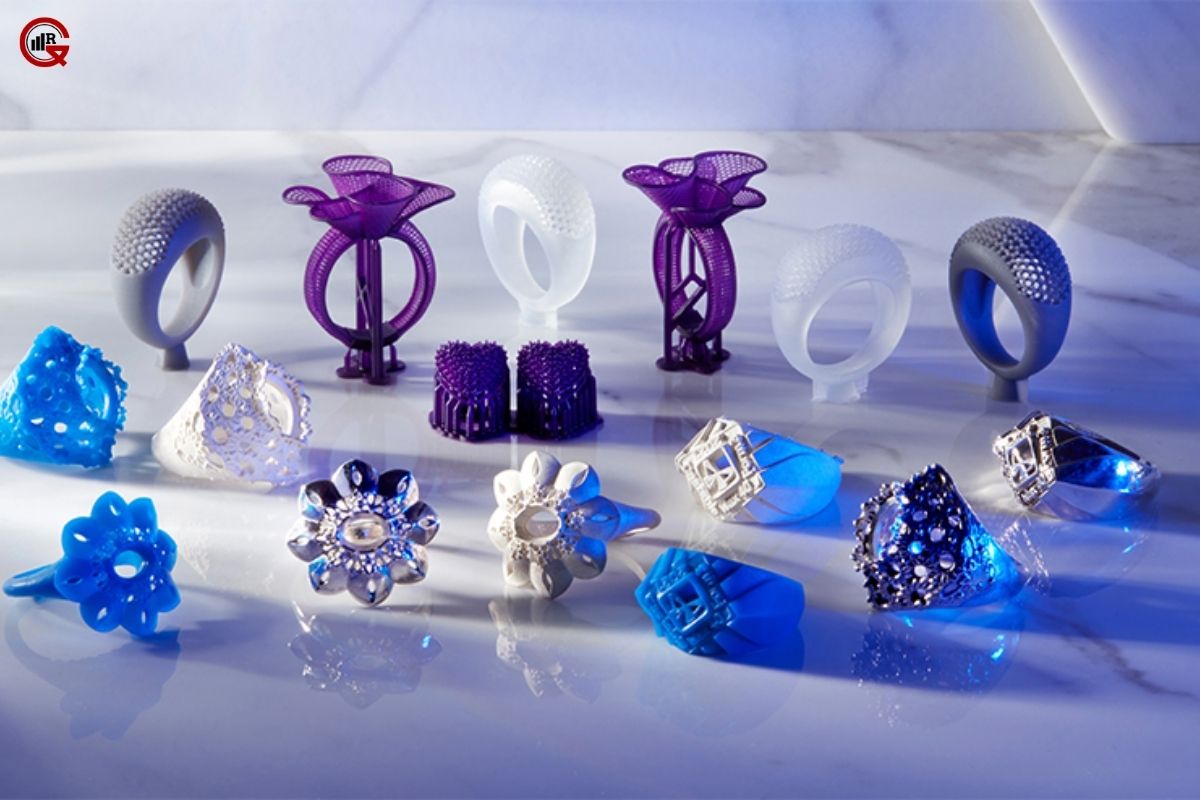

Mass Customization: Jewelry brands are leveraging 3D printing to offer mass customization options, where customers can select from a range of base designs and customize elements such as size, material, and finish.
Sustainable Jewelry: The material efficiency and reduced waste associated with 3D printing make it an attractive option for sustainable Jewelry production. Additionally, the ability to use recycled materials and minimize the environmental impact aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly products.
Future Prospects:
The future of 3D printed Jewelry is filled with exciting possibilities driven by ongoing advancements in materials science, printing technologies, and design methodologies. Some key trends and future directions include:
Advanced Materials: The development of new materials, including high-strength polymers, biocompatible metals, and innovative composites, will expand the range of applications for 3D printed Jewelry. These materials can enhance the durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal of the pieces.
Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining 3D printing with traditional Jewelry-making techniques, such as hand-finishing and stone setting, can create hybrid manufacturing processes that offer the best of both worlds. This approach allows for greater design flexibility and craftsmanship.
Integration with Digital Technologies: The integration of 3D printing with digital technologies such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) will enhance the customer experience. Customers can visualize and interact with digital models of their custom Jewelry before making a purchase.
Wearable Technology: The rise of wearable technology presents opportunities for incorporating smart features into 3D printed Jewelry. This includes integrating sensors, connectivity, and other functionalities to create Jewelry that is not only beautiful but also functional.
Sustainability and Ethical Practices: As consumers become more conscious of sustainability and ethical practices, 3D printing offers a way to produce Jewelry with a reduced environmental footprint. The use of recycled materials and on-demand production can further support sustainable and ethical manufacturing.
Conclusion:
3D printed Jewelry represents a groundbreaking advancement in the world of fashion and luxury, offering unparalleled design freedom, customization, and efficiency. From bespoke creations and intricate designs to sustainable practices and innovative materials, the applications of this technology are vast and continually expanding. As advancements in 3D printing technology and materials science continue to evolve, the future of 3D printed Jewelry holds immense promise, paving the way for a new era of creativity, personalization, and sustainability in the Jewelry industry. The ongoing integration of this technology into design and manufacturing processes promises to enhance the way we create, wear, and experience Jewelry, revolutionizing the industry for years to come.






