In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, technology continues to play a pivotal role in transforming patient care, diagnosis, and treatment. Among the most promising advancements is the integration of medical robots into clinical practice. From assisting surgeons in the operating room to automating repetitive tasks in laboratories, medical robots are revolutionizing healthcare delivery in ways once thought unimaginable. In this article, we delve into the world of medical robots, exploring their applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of robotic-assisted medicine.
The Evolution of Medical Robots
Robots have come a long way since their inception in the 1980s. Initially used for tasks such as patient transport and medication delivery, their capabilities have expanded dramatically over the years. Today, healthcare robots encompass a diverse range of technologies, including surgical robots, rehabilitation robots, telepresence robots, and robotic exoskeletons, each designed to address specific healthcare needs.
Applications of Healthcare Robots
Surgical Robotics: Perhaps the most well-known application of medical robots is in surgery. Surgical robots, such as the da Vinci Surgical System, enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision and dexterity. These systems use advanced imaging, robotics, and computer-assisted technologies to guide surgical instruments with unparalleled accuracy, resulting in shorter recovery times and improved patient outcomes.
Rehabilitation Robotics: For patients recovering from injuries or neurological conditions, rehabilitation robots offer targeted therapy and assistance. Robotic exoskeletons, for example, help individuals regain mobility and strength by providing support and guidance during physical therapy sessions. These devices not only accelerate the rehabilitation process but also empower patients to regain independence and improve their quality of life.
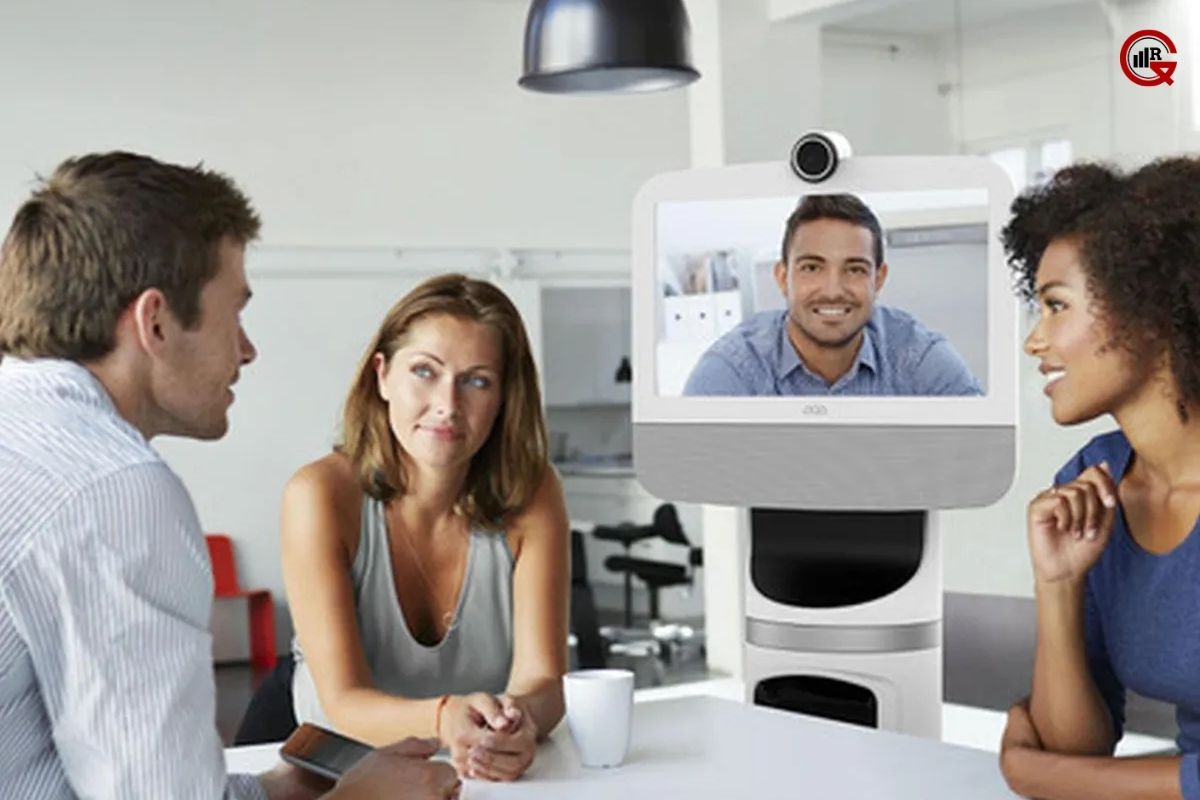

Telepresence Robots: In the era of telemedicine, telepresence robots are bridging the gap between patients and healthcare providers. These robots, equipped with cameras, screens, and audio systems, allow physicians to remotely interact with patients, conduct virtual consultations, and oversee medical procedures from anywhere in the world. Telepresence robots are particularly valuable in rural or underserved areas where access to specialized healthcare services is limited.
Laboratory Automation: Merobots are also revolutionizing laboratory workflows by automating repetitive tasks such as sample handling, testing, and analysis. Automated laboratory systems, powered by robotics and artificial intelligence, streamline processes, reduce errors, and improve efficiency, enabling healthcare professionals to focus on complex diagnostic and therapeutic tasks.
Benefits of Medical Robots
Precision and Accuracy: One of the key advantages of healthcare robots is their ability to perform tasks with unmatched precision and accuracy. In surgery, for example, robotic assistance allows surgeons to execute complex maneuvers with submillimeter accuracy, minimizing tissue damage and reducing the risk of complications.
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Surgical robots enable minimally invasive procedures, which involve smaller incisions, less blood loss, and faster recovery times compared to traditional open surgery. This not only benefits patients by reducing pain and scarring but also lowers the risk of postoperative infections and complications.
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Automation of repetitive tasks in healthcare settings improves efficiency and productivity, allowing healthcare professionals to focus their time and expertise on more complex and critical aspects of patient care. By freeing up valuable resources, healthcare robots help optimize workflow and reduce waiting times for patients.
Remote Access and Collaboration: Telepresence robots facilitate remote access to healthcare services, enabling consultations, diagnosis, and treatment planning regardless of geographical barriers. This is especially valuable in emergencies, disaster response situations, or during pandemics when physical distancing is necessary.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the numerous benefits they offer, healthcare robots also pose certain challenges and considerations:
Cost: The initial investment required to implement medical robotic systems can be substantial, limiting their adoption, especially in resource-constrained healthcare settings. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and upgrades contribute to the total cost of ownership, which may be prohibitive for some institutions.
Training and Education: Healthcare professionals need specialized training and education to effectively utilize medical robots. Surgeons, in particular, must undergo extensive training to master robotic-assisted surgical techniques and ensure patient safety. Integrating robotics into medical curricula and continuing education programs is essential to address this challenge.

Regulatory and Ethical Considerations: As with any medical technology, regulatory approval and ethical considerations are paramount. Ensuring the safety, efficacy, and ethical use of healthcare robots requires stringent regulatory oversight, standardized protocols, and adherence to ethical principles such as patient autonomy and informed consent.
Integration into Healthcare Systems: Integrating healthcare robots into existing healthcare systems and workflows can be complex and challenging. Compatibility with electronic health record systems, interoperability with other medical devices, and alignment with clinical protocols are critical factors to consider during implementation.
The Future of Medical Robots
Despite these challenges, the future of healthcare robots looks promising. Continued advancements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and sensor technologies are driving innovation and expanding the capabilities of healthcare robots. As costs decline and usability improves, healthcare robots are expected to become more accessible and widespread, transforming healthcare delivery on a global scale.
Expanding Applications and Innovations
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: In the realm of pharmaceuticals, medical robots are revolutionizing drug discovery, development, and production. Automated systems equipped with robotic arms and precision dispensers enable high-throughput screening of potential drug candidates, accelerating the pace of research and development. Additionally, robotic platforms facilitate precise formulation and compounding of medications, ensuring consistency and quality in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Assistive Robotics for Elderly Care: With an aging population worldwide, there is a growing need for assistive technologies to support independent living and improve the quality of life for older adults. Assistive robots, equipped with sensors, cameras, and AI algorithms, can assist with activities of daily living such as bathing, dressing, and medication reminders. These robots not only provide physical assistance but also offer companionship and social engagement, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation among elderly individuals.
Addressing Accessibility and Equity

Global Access to Healthcare: Healthcare robots have the potential to bridge the gap in access to healthcare services, particularly in underserved or remote areas. Telepresence robots enable virtual consultations and medical interventions, allowing patients to receive timely care without the need for travel. By democratizing access to specialized medical expertise, healthcare robots have the power to improve health outcomes and reduce disparities in healthcare access.
Affordability and Affordability: While the initial cost of healthcare robots may be a barrier to adoption, ongoing advancements in technology and manufacturing are driving down costs and making them more affordable. Additionally, innovative financing models and public-private partnerships can help ensure equitable access to medical robots, particularly in low-resource settings where they are most needed. By prioritizing affordability and accessibility, stakeholders can maximize the impact of healthcare robots on global health outcomes.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, medical robots represent a groundbreaking paradigm shift in healthcare, offering precision, efficiency, and accessibility like never before. From the operating room to the laboratory and beyond, healthcare robots are empowering healthcare professionals, enhancing patient outcomes, and shaping the future of medicine. With ongoing innovation, collaboration, and ethical stewardship, medical robots are poised to revolutionize healthcare delivery and improve the lives of millions around the world.