In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, technological advancements continue to drive innovation and efficiency across various industries. High-frequency welders represent a pinnacle of such advancements, offering a versatile and precise solution for joining materials in diverse applications. From automotive and aerospace to electronics and packaging, high-frequency welders have revolutionized the way materials are bonded, providing superior strength, speed, and quality. In this article, we delve into the principles, applications, and benefits of welders, exploring their transformative impact on modern manufacturing processes.
Understanding High-Frequency Welder :
High-frequency welding, also known as RF (radio frequency) welding or dielectric welding, is a specialized process that utilizes high-frequency electromagnetic waves to generate heat and bond materials together. Unlike conventional welding techniques that rely on melting the material itself, high-frequency welding operates on the principle of dielectric heating, where polar molecules within the material rapidly align and generate heat in response to an alternating electromagnetic field.
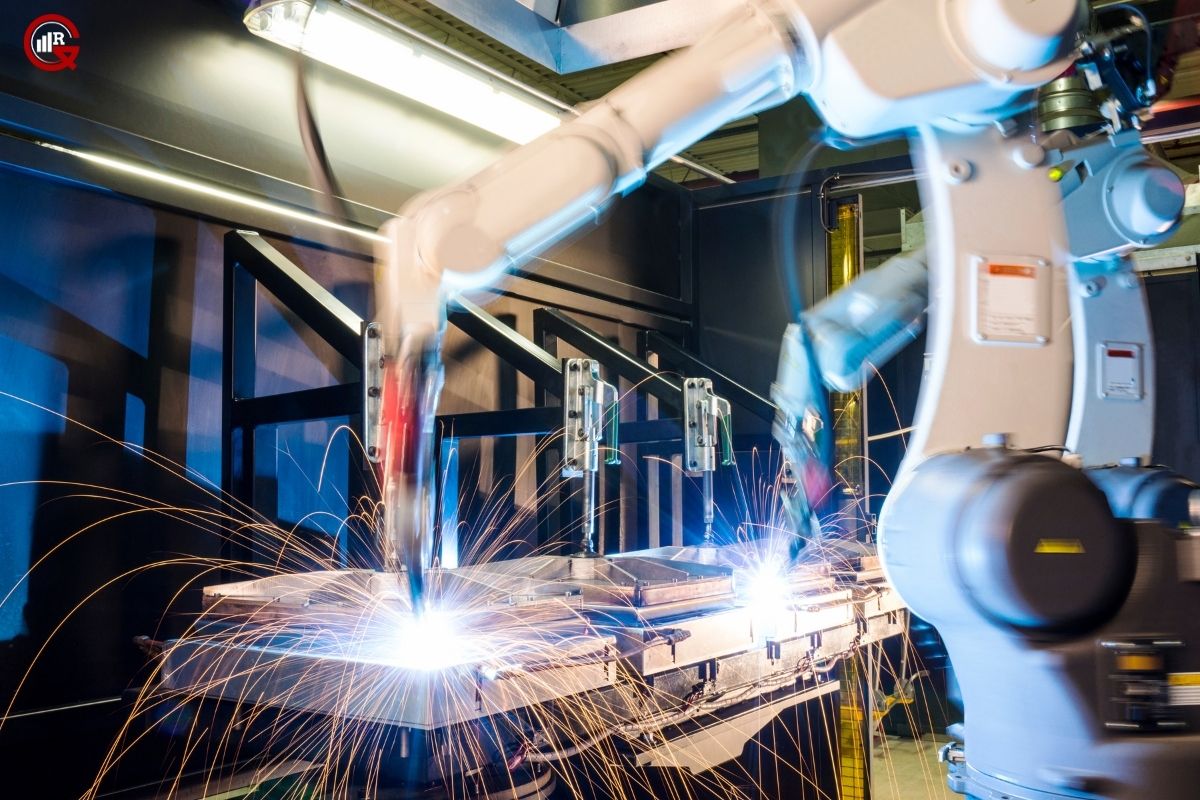

The core components of a high-frequency welding system include a high-frequency generator, welding electrodes, and a press mechanism. The generator produces high-frequency electrical energy, typically in the range of 27 to 100 megahertz (MHz), which is transmitted to the welding electrodes. These electrodes apply pressure to the materials being joined, while simultaneously delivering the high-frequency energy to induce localized heating and fusion along the bonding interface.
Key Advantages and Applications:
High-frequency welders offer a multitude of advantages over traditional welding methods, making them indispensable in a wide range of manufacturing processes. One of the primary benefits is the ability to achieve strong, durable bonds without the need for additional adhesives or fillers. This results in seamless joints with superior mechanical properties, resistance to corrosion, and aesthetic appeal, particularly in applications where cleanliness and hygiene are paramount, such as medical device manufacturing and food packaging.
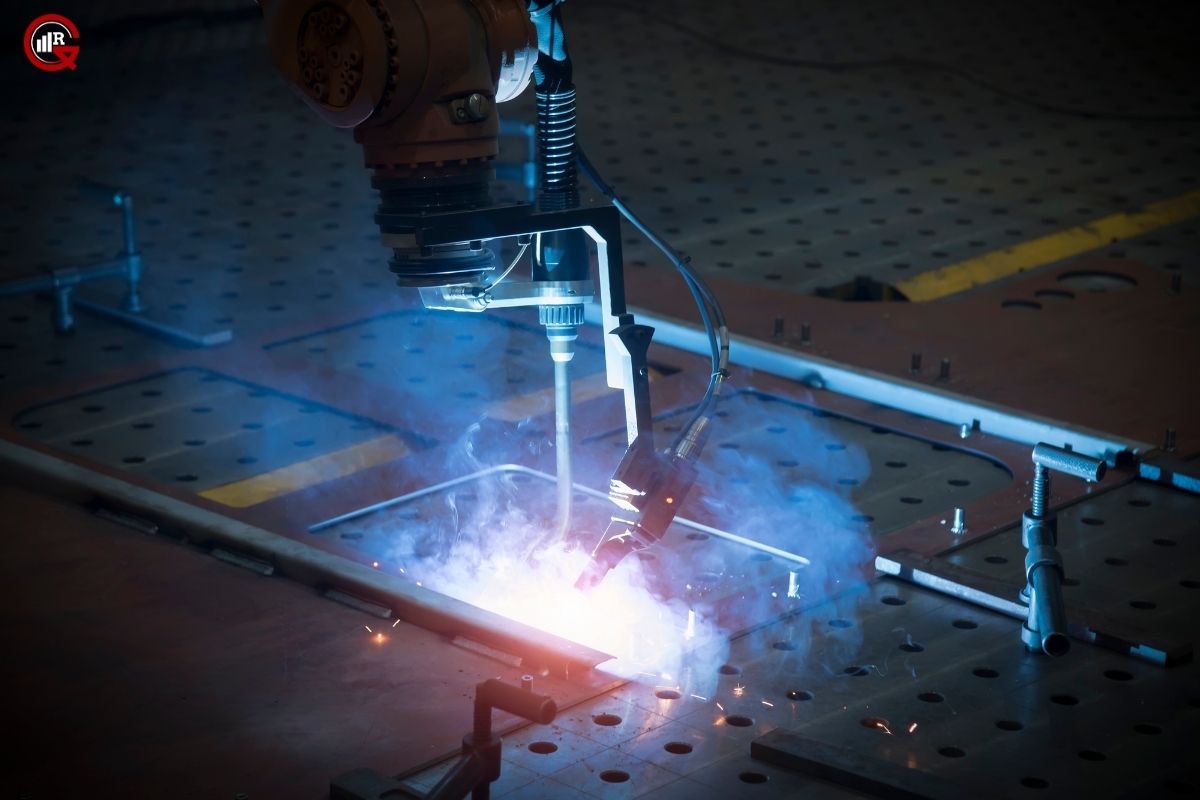

Moreover, high-frequency welding enables rapid and precise assembly of complex geometries, including three-dimensional contours and irregular shapes. This versatility makes it ideal for automotive components, inflatable structures, and consumer goods, where seamless integration of multiple parts is essential. Additionally, high-frequency welders excel in joining thermoplastic materials, such as PVC, TPU, PET, and polyethylene, offering exceptional bond strength and weld consistency across various material thicknesses and compositions.
In the automotive industry, high-frequency welders are widely employed for the fabrication of interior trim components, door panels, air ducts, and seating assemblies. The ability to produce airtight seals and watertight joints makes them indispensable for applications requiring superior durability, weather resistance, and acoustic insulation. Furthermore, high-frequency welding is extensively utilized in the production of inflatable structures, such as air mattresses, inflatable boats, and advertising inflatables, where rapid assembly and airtight seals are essential.
Emerging Trends and Future Directions:
As manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, high-frequency welders are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of advanced manufacturing processes. Recent advancements in materials science, automation, and digitalization have expanded the capabilities and applications of high-frequency welding systems, paving the way for new opportunities in sectors such as aerospace, electronics, and renewable energy.
In the aerospace industry, high-frequency welders are increasingly used for the fabrication of lightweight composite structures, such as aircraft interiors, fuselage panels, and engine components. The ability to bond thermoplastic composites with precision and efficiency offers significant advantages in terms of weight reduction, fuel efficiency, and structural integrity, thereby driving innovation in aircraft design and manufacturing.
Furthermore, the integration of robotics and artificial intelligence into high-frequency welding systems enables autonomous operation, adaptive control, and real-time quality monitoring. Advanced sensors and machine vision systems provide valuable insights into process parameters, weld integrity, and defect detection, ensuring consistent performance and product quality across high-volume production environments.
Conclusion:
High-frequency welders represent a transformative technology that has revolutionized the way materials are joined in modern manufacturing processes. By harnessing the power of electromagnetic waves, these systems offer unparalleled precision, efficiency, and versatility in bonding thermoplastic materials across diverse applications. From automotive and aerospace to consumer goods and medical devices, high-frequency welders have become indispensable tools for achieving seamless, durable, and aesthetically pleasing joints. As research and development efforts continue to push the boundaries of innovation, the transformative impact of high-frequency welding technology on manufacturing is poised to accelerate, driving efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness in global markets.






