Medical equipment plays a vital role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of various medical conditions, contributing to improved healthcare outcomes and patient well-being. From diagnostic tools and therapeutic devices to surgical instruments and monitoring systems, medical devices encompass a wide range of technologies designed to support healthcare professionals in delivering high-quality care. In this article, we will explore the importance, types, advancements, and impact of medical equipment in modern healthcare settings.
Importance of Medical Equipment:
Medical equipment serves as essential tools for healthcare providers in delivering accurate diagnoses, effective treatments, and personalized care to patients. These devices help healthcare professionals:
Diagnose Medical Conditions: Diagnostic equipment such as X-ray machines, MRI scanners, ultrasound devices, and laboratory analyzers enable healthcare providers to visualize internal structures, detect abnormalities, and diagnose various medical conditions accurately. These tools play a crucial role in early detection, disease screening, and treatment planning.
Monitor Patient Health: Monitoring equipment such as electrocardiography (ECG) machines, blood pressure monitors, pulse oximeters, and continuous glucose monitors allow healthcare providers to track vital signs, physiological parameters, and disease progression in real time. Continuous monitoring facilitates timely interventions, prevents complications, and optimizes patient outcomes.
Administer Treatments: Therapeutic equipment such as infusion pumps, ventilators, dialysis machines, and radiation therapy devices deliver medications, fluids, oxygen, and other treatments to patients with precision and control. These devices support therapeutic interventions, alleviate symptoms, and improve patient comfort and well-being.
Perform Surgical Procedures: Surgical instruments, operating room equipment, and minimally invasive devices enable surgeons to perform complex surgical procedures with precision, efficiency, and safety. These tools facilitate tissue manipulation, hemostasis, visualization, and tissue repair, ensuring optimal surgical outcomes and patient recovery.
Types of Medical Equipment:
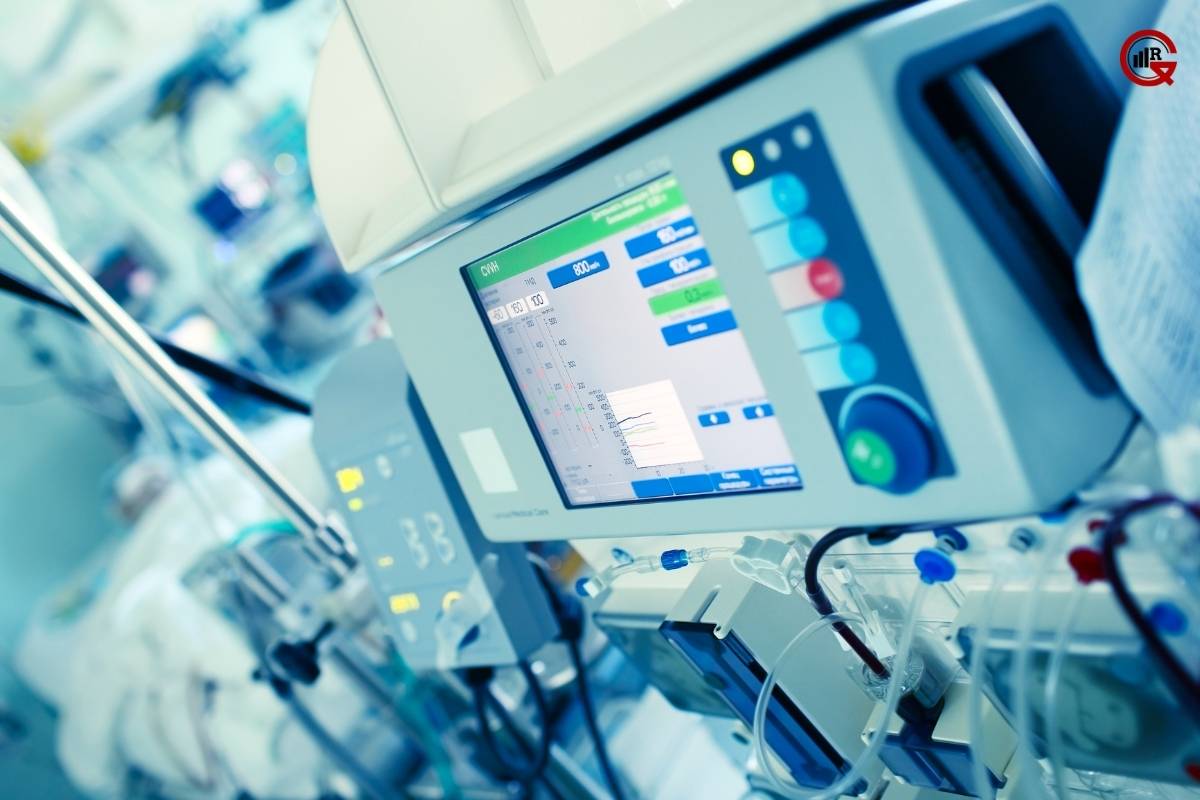

Medical device encompasses a diverse array of devices, instruments, and technologies designed for specific medical purposes. Some common types of medical equipment include:
Diagnostic Equipment: Used for imaging, laboratory testing, and diagnostic procedures, including X-ray machines, CT scanners, MRI scanners, ultrasound devices, blood analyzers, and endoscopes.
Monitoring Equipment: Used for continuous monitoring of vital signs, physiological parameters, and patient status, including ECG machines, blood pressure monitors, pulse oximeters, Holter monitors, and telemetry systems.
Therapeutic Equipment: Used for delivering treatments, medications, and therapies to patients, including infusion pumps, ventilators, dialysis machines, CPAP machines, radiation therapy devices, and nebulizers.
Surgical Equipment: Used for performing surgical procedures, including surgical instruments, operating tables, anesthesia machines, electrosurgical units, laparoscopic instruments, and robotic surgery systems.
Rehabilitation Equipment: Used for physical therapy, rehabilitation, and mobility assistance, including wheelchairs, walkers, crutches, orthotic devices, prosthetic limbs, and assistive devices for activities of daily living.
Patient Care Equipment: Used for patient comfort, safety, and hygiene, including hospital beds, patient lifts, bedside commodes, pressure relieving mattresses, and medical carts.
Advancements in Medical Equipment:
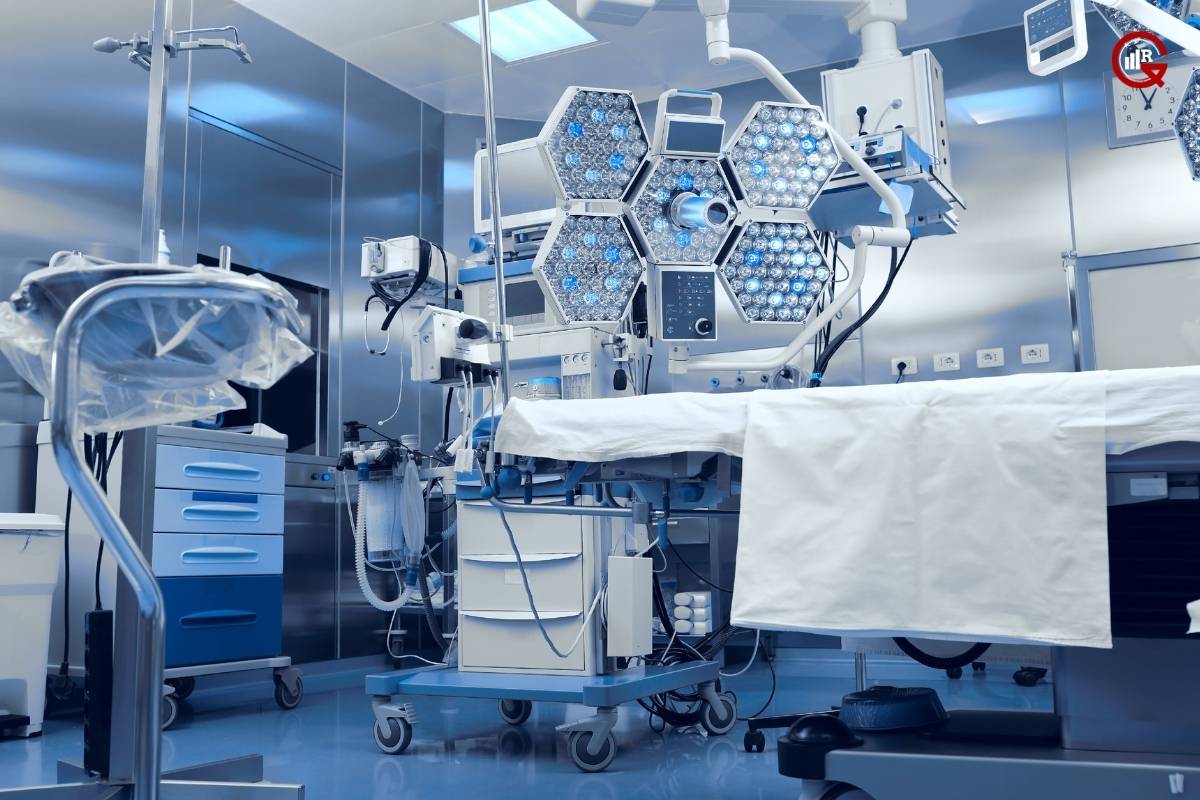
Advances in technology have led to significant innovations and advancements in medical equipment, enhancing their functionality, performance, and usability. Some notable advancements include:
Miniaturization and Portability: Many medical devices have become smaller, lighter, and more portable, allowing for increased mobility, flexibility, and accessibility in various healthcare settings, including ambulatory care, home care, and remote monitoring.
Connectivity and Integration: Medical device now features enhanced connectivity and interoperability, enabling seamless data exchange, integration with electronic health records (EHRs), and remote monitoring capabilities. This connectivity enhances care coordination, decision-making, and patient outcomes.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies are being integrated into medical devices to analyze data, identify patterns, and provide predictive insights for diagnosis, treatment planning, and personalized medicine. These technologies enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline workflows, and support evidence-based decision-making.
Wearable Devices and Remote Monitoring: Wearable medical devices, such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and continuous glucose monitors, enable continuous monitoring of vital signs, activity levels, and health metrics outside of traditional healthcare settings. These devices empower patients to take control of their health, monitor chronic conditions, and communicate with healthcare providers remotely.
Robotics and Automation: Robotics and automation technologies are revolutionizing surgical procedures, rehabilitation therapies, and patient care tasks, enhancing precision, efficiency, and safety. Robotic surgery systems, exoskeletons, and robotic prosthetics are examples of advancements in this area.
Impact of Medical Equipment:

The impact of medical devices on healthcare delivery and patient care is profound and far-reaching, contributing to:
Improved Clinical Outcomes: Medical device enables early detection, accurate diagnosis, and timely intervention, leading to improved clinical outcomes, reduced complications, and enhanced patient survival rates.
Enhanced Patient Safety and Comfort: Advanced monitoring, therapeutic, and patient care equipment promote patient safety, comfort, and satisfaction by minimizing risks, ensuring proper treatment delivery, and optimizing care delivery processes.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity: Medical device streamlines clinical workflows, automate routine tasks, and facilitate data-driven decision-making, resulting in increased efficiency, productivity, and resource utilization within healthcare organizations.
Expanded Access to Care: Portable, remote monitoring and telehealth-enabled medical devices extend access to healthcare services beyond traditional clinical settings, reaching underserved populations, rural communities, and patients with limited mobility or transportation options.
Cost Savings and Resource Optimization: Effective use of medical equipment can lead to cost savings, resource optimization, and reduced healthcare expenditures by preventing unnecessary hospitalizations, minimizing treatment complications, and improving care coordination and patient outcomes.
Conclusion:
Medical equipment plays a crucial role in modern healthcare delivery, enabling healthcare professionals to diagnose, treat, and manage medical conditions effectively while enhancing patient safety, comfort, and outcomes. With ongoing advancements in technology and innovation, medical device continues to evolve, offering new capabilities, functionalities, and opportunities to improve healthcare delivery and patient care. By investing in high-quality, reliable, and innovative medical equipment, healthcare organizations can optimize clinical workflows, enhance patient experiences, and achieve better healthcare outcomes for individuals and communities alike.






