In an era marked by increasing security threats and evolving risks, ensuring the safety of physical assets has become a paramount concern for organizations and individuals alike. Among the various layers of security, perimeter security stands as the first line of defense, forming a critical barrier against unauthorized access and potential threats. From residential properties to commercial establishments, the effectiveness of perimeter security measures plays a pivotal role in safeguarding assets, infrastructure, and most importantly, the people within.
The defense area encompasses a range of strategies and technologies designed to detect, deter, and respond to intrusions along the boundaries of a property. While traditional methods such as fences and gates remain fundamental components, advancements in technology have introduced sophisticated solutions capable of providing enhanced protection and real-time threat intelligence. In this article, we explore the importance of perimeter security and delve into effective strategies for bolstering protection in today’s dynamic threat landscape.
Understanding the Significance of Perimeter Security
The perimeter serves as the initial point of contact between a facility and potential threats. A robust security system not only prevents unauthorized access but also acts as a psychological deterrent, dissuading would-be intruders from attempting breaches. Moreover, by establishing clear boundaries and controlled access points, defense area measures enable efficient monitoring and response, minimizing the risk of security breaches and unauthorized activities.
In addition to safeguarding physical assets, the defense area plays a crucial role in ensuring regulatory compliance, protecting sensitive information, and preserving the privacy of occupants. For industries such as critical infrastructure, healthcare, and government facilities, the consequences of perimeter breaches can be severe, ranging from data breaches to operational disruptions and even threats to public safety. Therefore, investing in robust defense area solutions is not just a matter of protection but also a proactive measure to mitigate potential liabilities and safeguard reputations.
Key Components of Effective Perimeter Security

Physical Barriers: Traditional elements like fences, walls, and gates form the foundation of perimeter security. These barriers establish clear boundaries and control access, making it more difficult for unauthorized individuals to breach the perimeter. Modern advancements in materials and design have led to the development of high-security fences and barriers resistant to tampering, cutting, and climbing.
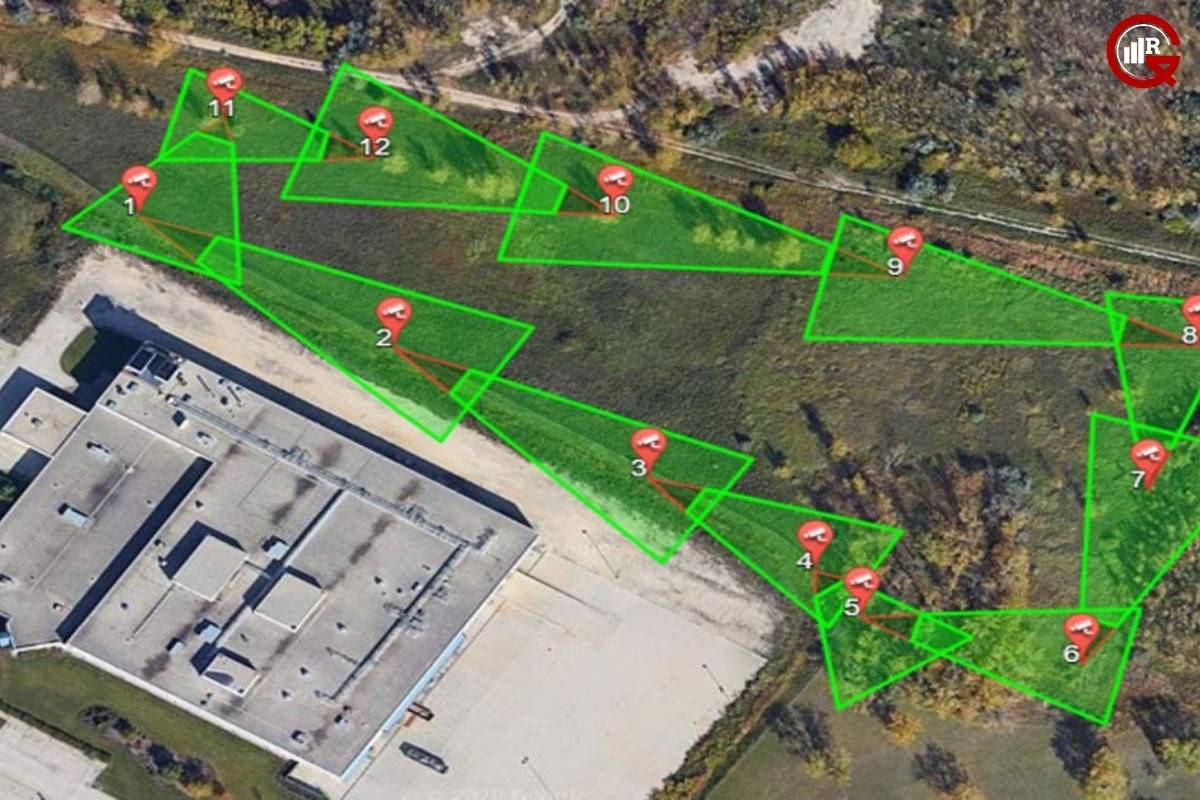
Surveillance Systems: Closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, motion sensors, and infrared detectors are integral components of a comprehensive perimeter surveillance system. These devices provide continuous monitoring of the perimeter, enabling real-time detection of suspicious activities and potential intrusions. Coupled with analytics software and remote monitoring capabilities, surveillance systems offer enhanced situational awareness and facilitate prompt response to security threats.
Access Control Systems: Access control systems regulate entry and exit points, allowing only authorized individuals to access the premises. From keypad entry systems to biometric scanners and smart card readers, modern access control technologies offer diverse options for controlling access based on user credentials and permissions. Integration with surveillance systems and alarm systems further enhances security by logging access events and triggering alerts in case of unauthorized attempts.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): IDS utilize sensors and alarms to detect unauthorized entry attempts or breaches of the perimeter. These systems can be configured to detect specific threats such as forced entry, perimeter breaches, or tampering with security infrastructure. Upon detection, IDS triggers immediate alerts to security personnel or initiates automated responses such as activating lights, and sirens, or notifying law enforcement.
Perimeter Lighting: Adequate lighting along the perimeter enhances visibility and acts as a deterrent to intruders. Motion-activated lights and programmable lighting systems can effectively illuminate vulnerable areas during nighttime or low-light conditions, reducing blind spots and improving surveillance coverage.
Implementing a Comprehensive Perimeter Security Plan

Effective defense area requires a holistic approach that integrates multiple layers of protection tailored to the specific needs and vulnerabilities of the property. Here are some essential steps to consider when implementing a comprehensive perimeter security plan:
Risk Assessment: Conduct a thorough assessment of the property to identify potential security vulnerabilities, including weak points in the perimeter, blind spots in surveillance coverage, and access control deficiencies. Evaluate the level of risk posed by various threats such as theft, vandalism, unauthorized access, and terrorist activities.
Security Policy Development: Establish clear security policies and protocols governing perimeter security measures, access control procedures, and incident response protocols. Ensure that all stakeholders, including employees, tenants, and security personnel, are trained in security awareness and compliance with established policies.
Integration of Technologies: Invest in modern security technologies that offer seamless integration and interoperability, allowing for centralized monitoring and management of teh defense area systems. Implement a security information and event management (SIEM) system to consolidate security alerts and streamline incident response processes.
Regular Maintenance and Testing: Conduct routine maintenance checks and performance testing of perimeter security systems to ensure optimal functionality and reliability. Regularly update firmware and software patches to address vulnerabilities and mitigate potential security risks.
Collaboration with Law Enforcement: Establish partnerships with local law enforcement agencies and emergency responders to enhance coordination and support during security incidents. Share relevant information and intelligence to facilitate proactive threat mitigation and investigation of security breaches.
Future Trends and Emerging Technologies
As security threats continue to evolve, the field of security is witnessing rapid advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT). Predictive analytics and AI-driven threat detection algorithms enable the proactive identification of potential security threats based on anomalous behavior patterns and trends. Similarly, IoT-enabled sensors and devices offer real-time monitoring of environmental conditions and perimeter status, enabling dynamic adjustments to security protocols and response strategies.
Furthermore, the integration of physical security systems with cybersecurity measures is becoming increasingly important to mitigate the risk of cyber-physical attacks targeting the defense area infrastructure. By adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses both physical and digital security threats, organizations can strengthen their resilience and adaptability in the face of evolving security challenges.
Conclusion
In an age of heightened security concerns and complex threats, the importance of perimeter security cannot be overstated. By implementing robust defense area measures and adopting a proactive, multi-layered approach, organizations can enhance the protection of their assets, infrastructure, and people. From physical barriers and surveillance systems to access control technologies and intrusion detection systems, leveraging the latest advancements in security technology is essential to stay ahead of emerging threats and safeguard against potential vulnerabilities. By prioritizing perimeter security as a fundamental component of their overall security strategy, organizations can mitigate risks, ensure regulatory compliance, and foster a safe and secure environment for their stakeholders.






